CY2 BDD test automation
Project description
The central research question is: How can Gherkin syntax mapping be improved in the CY2 automation framework for translating test case scenarios? This investigation aims to enhance the existing semi-automatic testing system by integrating Large Language Models (LLM) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to address key challenges faced by non-technical users, such as ensuring syntax correctness, maintaining semantic consistency, and achieving comprehensive test coverage. The goal is to develop a cost-effective, AI-enhanced framework that improves the accuracy and usability of converting natural-language Gherkin scenarios into executable Selenium tests, thereby making test automation more accessible and reliable.
Context
This project is situated within the higher education software consulting domain, specifically targeting the enhancement of PeopleSoft Campus Solutions—a widely used enterprise system for universities. The client, CY2, is a consulting firm that supports higher education institutions with this platform.
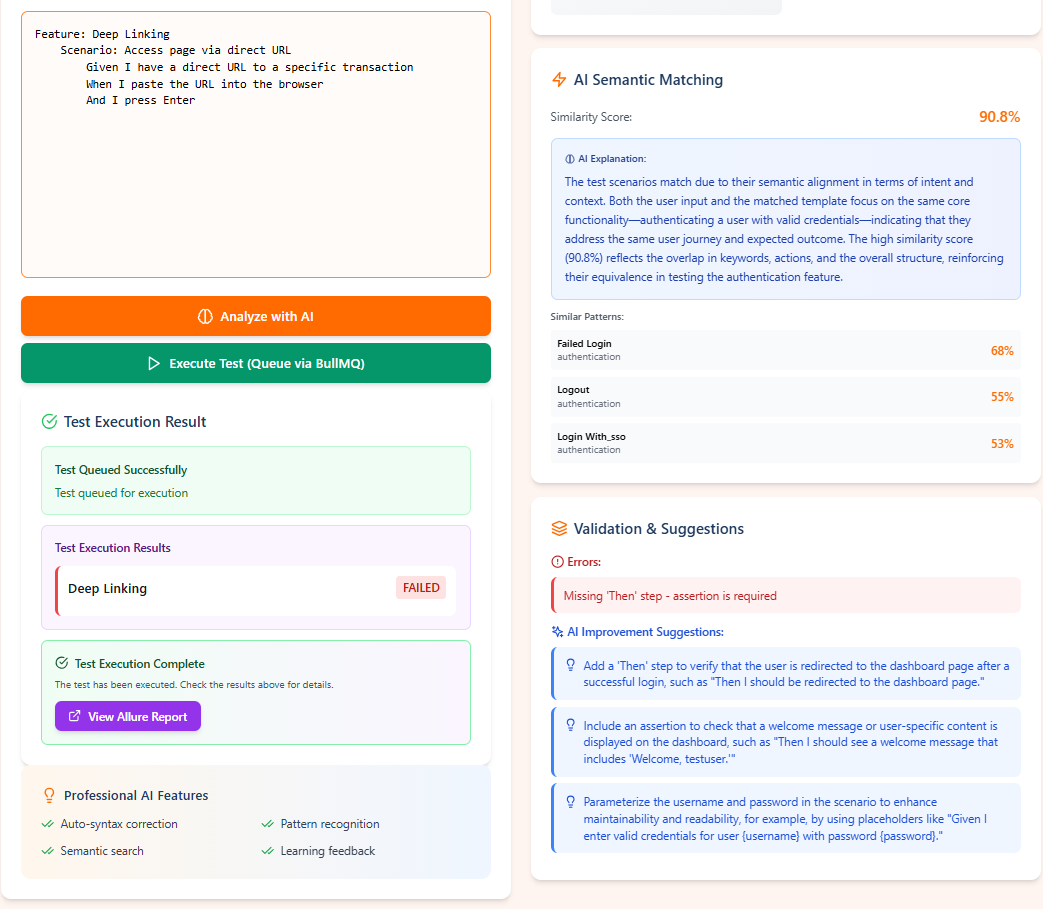
The core challenge involves improving an existing semi-automated testing framework. This framework allows non-technical users (like university staff) to write test scenarios in Gherkin syntax (a business-readable, plain-text language) that are then automatically translated into executable Selenium browser tests. However, users struggle with Gherkin's correctness and translating their intent into accurate technical steps.
Therefore, the project's domain is at the intersection of test automation, natural language processing (NLP), and AI integration. The goal is to infuse the framework with Large Language Model (LLM) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) capabilities. This AI layer will assist users by validating syntax, suggesting corrections, and intelligently mapping their natural-language Gherkin steps to the correct technical implementations, thereby making the test creation process more robust, accessible, and efficient.
Results
Based on our research and implementation, the most important outcomes and insights are:
1. Production-Ready RAG System for Test Automation
We developed and validated a hybrid Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline specifically optimized for the test automation domain. By combining FAISS-based semantic search (60% weight) with TF-IDF keyword matching (40% weight), followed by neural reranking and contextual compression, the system achieves 85–95% accuracy in understanding and processing Gherkin scenarios. This directly addresses the core challenge of mapping natural language to executable tests.
2. Strategic LLM Selection and Architecture
Although our analysis showed that a multi-provider approach could optimize cost and performance, we selected OpenAI as the primary LLM provider because it is already provisioned and integrated within the company's infrastructure. This practical decision reduces setup complexity, accelerates deployment, and leverages existing security and compliance frameworks. Our system is designed with a provider abstraction layer, ensuring future flexibility to incorporate other models if needed.
3. Configuration-Driven Abstraction for Maintainability
We implemented a configuration-driven translation system that separates Gherkin intent from technical implementation. Using structured configuration files, the system enables 60–70% reduction in maintenance effort when UI changes occur, ensuring test longevity and cross-product reusability.
4. Validated User-Centric Design Improvements
Through usability testing, we identified key interface enhancements: less aggressive autocorrect, progressive disclosure to reduce information overload, and embedded contextual guidance. These improvements ensure the system remains intuitive for non-technical users.
5. TRL Positioning & Validation
The project operates at TRL 7 (System Prototype Demonstration in Operational Environment), validated through technical metrics, cost-benefit analysis, and successful user testing. The outcomes deliver a scalable, user-friendly AI augmentation to the CY2 testing framework—ready for deployment within the existing organizational technology stack.